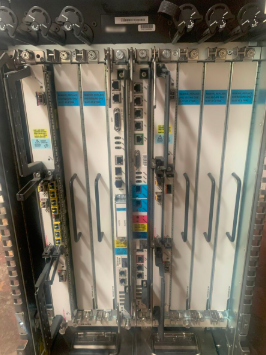
The Cisco® Carrier Routing System (CRS) offers industry-leading performance, advanced services intelligence, environmentally conscious design, and system longevity. The Cisco CRS is powered by a chipset architecture based on multidimensional engineering and Cisco IOS® XR Software, a unique self-healing, distributed operating system.
Packet-based data communications are being replaced by video and interactive multimedia transported on the Next-Generation Network (NGN) in multiple directions. This new traffic strains the architectural foundations of both public and private networks serving businesses and consumers. As part of a media-aware Cisco Next Generation Network, the Cisco CRS delivers highly reliable operations and scales easily from single-chassis form factors to a massive multi-chassis system. The Cisco CRS also referred to as the CRS-1, CRS-3, and CRS-X is a system that is both forward and backward compatible, built for investment protection and designed to provide industry-leading efficiencies in scaling, energy use, cooling, and rack-space resources.
The Cisco CRS 8-Slot Single-Shelf System (Figure 1) offers many advantages:
● The system is powered by a chipset architecture engineered for the Cisco CRS Router Family, which provides higher bandwidth than competing products, without compromising service performance. The Cisco CRS chipset is based on multidimensional engineering that includes several functional components working in tandem throughout the platform.
● The system uses Cisco IOS XR Software, the only fully modular, fully distributed internetwork operating system using a memory-protected, microkernel-based architecture and control-plane distribution that allows the system to scale and provide always-on operation.
● This single-shelf system is compatible with existing and future line cards of the Cisco CRS Family.
● The fully redundant carrier-class configuration supports in-service upgrades from 40 Gbps to 400 Gbps per slot.
● Integrated technology includes IP and Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) routing, IP over dense wavelength-division multiplexing (IPoDWDM), network virtualization with secure domain routers (SDRs), fabric multicast replication, fabric quality of service (QoS), Cisco NetFlow accounting, and Carrier-Grade IPv6 (CGv6) to provide an outstanding quality of experience (QoE) at the lowest possible total cost of ownership (TCO).
● The system can also scale with back-to-back system capability, connecting two CRS 8-Slot Chassis directly, using switch fabric cards and optical cables to form a single logical system.
| CRS-8/S-B CRS | CRS-8/SCRS |
Feature | Description | |
Product compatibility | Compatible with all current Cisco CRS Family modular services cards (MSCs), forwarding processors, physical layer interface modules (PLIMs), Label Switch Processors (CRS-LSPs), route processors, and fabric cards | Compatible with all current Cisco CRS Family modular services cards (MSCs), forwarding processors, physical layer interface modules (PLIMs), CRS Label Switch Processors (CRS-LSPs), route processors, and fabric cards |
Back-to-Back Compatibility | Yes | Yes |
Software compatibility | Cisco IOS XR Software Release 4.1.2 or later | Cisco IOS XR Software Release 4.0.0 or later * Cisco IOS XR Software Release 3.0.0 or later |
Protocols | ● Cisco Discovery Protocol ● IPv4 and IPv6 addressing ● Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) ● Layer 3 routing protocols, including: ◦ Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 (BGPv4) ◦ Multiprotocol BGP Version 4 (MP-BGP v4) ◦ Open Shortest Path First Version 2 (OSPFv2) ◦ OSPFv3 ◦ Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) Protocol ◦ Static Routes ◦ Routing Policy Language (RPL) ● Multicast forwarding with support for source-based and shared distribution trees and the following protocols: ◦ Protocol Independent Multicast sparse mode (PIM-SM) ◦ Bidirectional PIM (Bidir-PIM) ◦ PIM source-specific mode (PIM SSM) ◦ Automatic route processing (AutoRP) ◦ Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Versions 1, 2, and 3 ◦ Multiprotocol BGP (MBGP) ◦ Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) ● Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS): ◦ MPLS Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) ◦ Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) ◦ DiffServ-Aware Traffic Engineering (TE) ● MPLS Traffic Engineering control plane (RFCs 2702 and 2430) ● Route Policy Language (RPL) ● Management: ◦ Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ◦ Programmatic interfaces (XML) ● Security: ◦ Message Digest Algorithm (MD5) ◦ IP Security (IPsec) Protocol ◦ Secure Shell Protocol Version 2 (SSHv2) ◦ Secure FTP (SFTP) ◦ Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) | ● Cisco Discovery Protocol ● IPv4 and IPv6 addressing ● Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) ● Layer 3 routing protocols, including: ◦ Border Gateway Protocol Version 4 (BGPv4) ◦ Multiprotocol BGP Version 4 (MP-BGP v4 ◦ Open Shortest Path First Version 2 (OSPFv2) ◦ OSPFv3 ◦ Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) Protocol ◦ Static Routes ◦ Routing Policy Language (RPL) ● Multicast forwarding with support for source-based and shared distribution trees and the following protocols: ◦ Protocol Independent Multicast sparse mode (PIM-SM) ◦ Bidirectional PIM (Bidir-PIM) ◦ PIM source-specific mode (PIM SSM) ◦ Automatic route processing (AutoRP) ◦ Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) Versions 1, 2, and 3 ◦ Multiprotocol BGP (MBGP) ◦ Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) ● Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS): ◦ MPLS Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) ◦ Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP) ◦ DiffServ-Aware Traffic Engineering (TE) ● MPLS Traffic Engineering control plane (RFCs 2702 and 2430) ● Route Policy Language (RPL) ● Management: ◦ Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) ◦ Programmatic interfaces (XML) ● Security: ◦ Message Digest Algorithm (MD5) ◦ IP Security (IPsec) Protocol ◦ Secure Shell Protocol Version 2 (SSHv2) ◦ Secure FTP (SFTP) ◦ Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) |
Components | Each Cisco CRS enhanced 8-slot line card chassis includes: ● 2 Cisco CRS 8-slot line card chassis route processors (CRS-8-RP) ● 4 Cisco CRS 8-slot fabric cards ● 2 power supplies (either DC or AC) ● 2 fan trays Optional items: ● 8 Cisco CRS line cards ● 8 Cisco CRS PLIMs | Each Cisco CRS 8-slot line card chassis includes: ● 1 Cisco CRS 8-slot line card chassis route processor (CRS-8-RP) ● 4 Cisco CRS 8-slot fabric cards ● 2 power supplies (either DC or AC) ● 2 fan trays Optional items include: ● 8 Cisco CRS line cards ● 8 Cisco CRS PLIMs |
Line Cards, ports, and slots | ● 1-port OC-768c/STM-256c packet over SONET (PoS) ● 4-port OC-192c/STM-64c PoS/Dynamic Packet Transport (DPT) ● 16-port OC-48c/STM-16 PoS/DPT ● 8-port 10 Gigabit Ethernet (GE) ● 4-port 10 GE ● 42-port 1 GE ● 1-port OC-768c/STM-256c Tunable WDMPoS ● 4-port 10 GE tunable WDMPHY ● 14-port 10 GE LAN/WAN PHY ● 20-port 10 GE LAN/WAN PHY ● 1-Port 100 Gigabit Ethernet Interface Module ● Cisco CRS-1-SIP-800 Carrier Card ● 2- and 4-port OC-3c/STM-1c PoS shared port adapters (SPAs) ● 1-port, 2-port, and 4-port OC-48c/STM-16c PoS/RPR SPA ● 1-port OC-192c/STM-64c PoS/RPR SPA ● 1-port 10 GE SPA ● 2-port and 4-port Clear Channel T3/E3 SPAs ● 2-port, 4-port, and 8-port OC-12c/STM-4 PoS SPAs ● 2-port, 5-port, 8-port, and 10-port GE SPAs ● 1-port 10 GE LAN/WAN-PHY SPA ● 20-port GE flexible interface module ● 2-port 10 GE WAN/LAN-PHY flexible interface module ● Flexible SPA and 6-port 10GE PLIM ● 2-Port 40GE LAN/OTN Interface Module ● 4-Port 40GE LAN/OTN Interface Module ● 1-Port 100 Gigabit Ethernet Coherent DWDM Interface Module ● 40×10 Gigabit Ethernet Interface Module ● 4-Port 100GE LAN/OTN Interface Module | ● 1-port OC-768c/STM-256c packet over SONET (PoS) ● 4-port OC-192c/STM-64c PoS/Dynamic Packet Transport (DPT) ● 16-port OC-48c/STM-16 PoS/DPT ● 8-port 10 Gigabit Ethernet (GE) ● 4-port 10 GE ● 42-port 1 GE ● 1-port OC-768c/STM-256c Tunable WDMPoS ● 4-port 10 GE tunable WDMPHY ● 14-port 10 GE LAN/WAN PHY ● 20-port 10 GE LAN/WAN PHY ● 1-Port 100 Gigabit Ethernet Interface Module ● Cisco CRS-1-SIP-800 Carrier Card ● 2- and 4-port OC-3c/STM-1c PoS shared port adapters (SPAs) ● 1-port, 2-port, and 4-port OC-48c/STM-16c PoS/RPR SPA ● 1-port OC-192c/STM-64c PoS/RPR SPA ● 1-port 10 GE SPA ● 2-port and 4-port Clear Channel T3/E3 SPAs ● 2-port, 4-port, and 8-port OC-12c/STM-4 PoS SPAs ● 2-port, 5-port, 8-port, and 10-port GE SPAs ● 1-port 10 GE LAN/WAN-PHY SPA ● 20-port GE flexible interface module ● 2-port 10 GE WAN/LAN-PHY flexible interface module ● Flexible SPA and 6-port 10GE PLIM ● 2-Port 40GE LAN/OTN Interface Module ● 4-Port 40GE LAN/OTN Interface Module ● 1-Port 100 Gigabit Ethernet Coherent DWDM Interface Module ● 40×10 Gigabit Ethernet Interface Module ● 4-Port 100GE LAN/OTN Interface Module |
Fabric Cards | CRS-8-FC/S CRS-8-140FC/S CRS-8-FC140/M CRS-8-FC400/S CRS-8-FC400/M | CRS-8-FC/S CRS-8-140FC/S CRS-8-FC140/M CRS-8-FC400/S CRS-8-FC400/M *Note: Legacy chassis is limited to 200G on CRS-8-FC400/S on CRS-8-FC400/M |
Connectivity | PoS, WDM, DPT, T3/E3, 100 GE, 10 GE, 1 GE | PoS, WDM, DPT, T3/E3, 100 GE, 10 GE, 1 GE |
Features and functions | IP features: ● Control-plane packet handling ● IPv4 host services ● IPv4 unicast forwarding ● IPv4 equal-cost multipath (ECMP) ● IPv6 host services ● IPv6 forwarding services ● IPv6 ECMP Forwarding features: ● Access control lists (ACLs) ● Quality of service (QoS) and class of service (CoS) using Modular QoS CLI (MQC) ● IP packet classification and marking ● Queuing (both ingress and egress) ● Policing (both ingress and egress) ● Diagnostic and network-management support IPv4 multicast features: ● Dynamic registration using IGMP ● Multicast Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) ● PIM sparse mode (SM) ● PIM source-specific mode (PIM SSM) ● Automatic route processing ● MSDP ● MBGP ● Bidirectional PIM ● Source Specific Multicast with IGMPv3 ● Explicit tracking of hosts, group, and channels for IGMPv3 ● Multicast nonstop forwarding (NSF) MPLS features: ● MPLS forwarding and load balancing ● LDP ● RSVP ● MPLS traffic-engineering features ● User-Network Interface (UNI) ● Link Management Protocol (LMP) Security features: ● Message Digest Algorithm 5 (MD5) ● Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) ● Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol and Secure FTP (SFTP) ● Secure HTTP (SHTTP) support ● Control packet policing ● IP Security (IPsec) Manageability features: ● Alarms management ● Configuration management ● Accounting and statistics management ● Performance management ● Control point and network management – Generic requirements ● Terminal services enhancements ● Enhanced command-line interface (CLI) ● Extensible Markup Language (XML) interface ● XML schemas ● Cisco Craft Works Interface (CWI) ● Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) support ● Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and MIB support | IP features: ● Control-plane packet handling ● IPv4 host services ● IPv4 unicast forwarding ● IPv4 equal-cost multipath (ECMP) ● IPv6 host services ● IPv6 forwarding services ● IPv6 ECMP Forwarding features: ● Access control lists (ACLs) ● Quality of service (QoS) and class of service (CoS) using Modular QoS CLI (MQC) ● IP packet classification and marking ● Queuing (both ingress and egress) ● Policing (both ingress and egress) ● Diagnostic and network-management support IPv4 multicast features: ● Dynamic registration using IGMP ● Multicast Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) ● PIM sparse mode (SM) ● PIM source-specific mode (PIM SSM) ● Automatic route processing ● MSDP ● MBGP ● Bidirectional PIM ● Source Specific Multicast with IGMPv3 ● Explicit tracking of hosts, group, and channels for IGMPv3 ● Multicast nonstop forwarding (NSF) MPLS features: ● MPLS forwarding and load balancing ● LDP ● RSVP ● MPLS traffic-engineering features ● User-Network Interface (UNI) ● Link Management Protocol (LMP) Security features: ● Message Digest Algorithm 5 (MD5) ● Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) ● Secure Shell (SSH) Protocol and Secure FTP (SFTP) ● Secure HTTP (SHTTP) support ● Control packet policing ● IP Security (IPsec) Manageability features: ● Alarms management ● Configuration management ● Accounting and statistics management ● Performance management ● Control point and network management: Generic requirements ● Terminal services enhancements ● Enhanced command-line interface (CLI) ● Extensible Markup Language (XML) interface ● XML schemas ● Cisco Craft Works Interface (CWI) ● Common Object Request Broker Architecture (CORBA) support ● Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and MIB support |
Options | Cisco CRS-1 8-Slot Line Card Chassis Route Processor (CRS‑8-RP) | Cisco CRS-1 8-Slot Line Card Chassis Route Processor (CRS‑8-RP) |
Performance | 6.4/2.24-Tbps switching capacity | 2.24-Tbps switching capacity |
Reliability and availability | System redundancy: ● Power-shelf redundancy 1:1 ● Fan-tray redundancy 1:1 ● Route-processor redundancy 1:1 ● Fabric-card redundancy 1:4 ● Dual homing with line cards ● Support for APS Software features: ● NSF using graceful restart for: IS-IS, OSPF, BGP, LDP, and RSVP ● SONET APS 1:1 ● Line-card OIR support ● Fabric-card OIR support ● Out-of-resource management ● Process restartability ● MPLS Fast Reroute (FRR) ● Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) | System redundancy: ● Power-shelf redundancy 1:1 ● Fan-tray redundancy 1:1 ● Route-processor redundancy 1:1 ● Fabric-card redundancy 1:4 ● Dual homing with line cards ● Support for APS Software features: ● NSF using graceful restart for: IS-IS, OSPF, BGP, LDP, and RSVP ● SONET APS 1:1 ● Line-card OIR support ● Fabric-card OIR support ● Out-of-resource management ● Process restartability ● MPLS Fast Reroute (FRR) ● Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) and Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) |
MIBs | SNMP framework support: ● SNMPv1 ● SNMPv2c ● SNMPv3 ● MIB II, including interface extensions (RFC 1213) ● SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB ● SNMP-TARGET-MIB ● SNMP-NOTIFICATION-MIB ● SNMP-USM-MIB ● SNMP-VACM-MIB System management: ● CISCO- BULK-FILE-MIB ● CISCO-CONFIG-COPY-MIB ● CISCO-CONFIG-MAN-MIB ● CISCO-FLASH-MIB ● CISCO-MEMORY-POOL-MIB ● Cisco FTP Client MIB ● Cisco Process MIB ● Cisco Syslog MIB ● CISCO-SYSTEM-MIB ● CISCO-CDP-MIB ● IF-MIB (RFC 2233/RFC 2863) Chassis: ● ENTITY-MIB (RFC 2737) ● CISCO-entity-asset-MIB ● CISCO-entity-sensor-MIB ● CISCO-FRU-MIB (Cisco-Entity-FRU-Control-MIB) Fabric: ● CISCO-Fabric-HFR-MIB ● CISCO-Fabric-Mcast-MIB ● CISCO-Fabric-Mcast-Appl-MIB Routing protocols: ● BGP4-MIB Version 1 ● OSPFv1MIB (RFC1253) ● CISCO-IETF-IP-FORWARDING-MIB ● IP-MIB (was RFC2011-MIB) ● TCP-MIB (RFC 2012) ● UDP-MIB ● CISCO-HSRP-EXT-MIB ● CISCO-HSRP-MIB ● CISCO-BGP-POLICY-ACCOUNTING-MIB QoS: ● MQC-MIB (Cisco Class-Based QoS MIB) ● CISCO-PING-MIB Traps: ● RFC 1157 ● Authentication ● Linkup ● Linkdown ● Coldstart ● Warmstart | SNMP framework support: ● SNMPv1 ● SNMPv2c ● SNMPv3 ● MIB II, including interface extensions (RFC 1213) ● SNMP-FRAMEWORK-MIB ● SNMP-TARGET-MIB ● SNMP-NOTIFICATION-MIB ● SNMP-USM-MIB ● SNMP-VACM-MIB System management: ● CISCO- BULK-FILE-MIB ● CISCO-CONFIG-COPY-MIB ● CISCO-CONFIG-MAN-MIB ● CISCO-FLASH-MIB ● CISCO-MEMORY-POOL-MIB ● Cisco FTP Client MIB ● Cisco Process MIB ● Cisco Syslog MIB ● CISCO-SYSTEM-MIB ● CISCO-CDP-MIB ● IF-MIB (RFC 2233/RFC 2863) Chassis: ● ENTITY-MIB (RFC 2737) ● CISCO-entity-asset-MIB ● CISCO-entity-sensor-MIB ● CISCO-FRU-MIB (Cisco-Entity-FRU-Control-MIB) Fabric: ● CISCO-Fabric-HFR-MIB ● CISCO-Fabric-Mcast-MIB ● CISCO-Fabric-Mcast-Appl-MIB Routing protocols: ● BGP4-MIB Version 1 ● OSPFv1MIB (RFC1253) ● CISCO-IETF-IP-FORWARDING-MIB ● IP-MIB (was RFC2011-MIB) ● TCP-MIB (RFC 2012) ● UDP-MIB ● CISCO-HSRP-EXT-MIB ● CISCO-HSRP-MIB ● CISCO-BGP-POLICY-ACCOUNTING-MIB QoS: ● MQC-MIB (Cisco Class-Based QoS MIB) ● CISCO-PING-MIB Traps: ● RFC 1157 ● Authentication ● Linkup ● Linkdown ● Coldstart ● Warmstart |
Network management | ● Enhanced CLI ● XML interface ● Cisco Craft Works Interface (CWI) ● SNMP and MIB support | ● Enhanced CLI ● XML interface ● Cisco Craft Works Interface (CWI) ● SNMP and MIB support |
Programming interfaces | XML schema support | XML schema support |
Physical dimensions | Chassis height: 38.5 in. (97.79 cm, with base cosmetics) Chassis width: 17.5 in. (44.45 cm) Chassis depth: 36.6 in (92.964 cm); 40.5 in. (102.87 cm), including full cosmetics Weight: ● 330.8 lb (148.86 kg) chassis with fans, PDUs, and blanks (as shipped) ● 650 lb (292.5 kg) chassis as shipped, including power shelves and all line cards and route processors | Chassis height: 38.5 in. (97.79 cm, with base cosmetics) Chassis width: 17.5 in. (44.45 cm) Chassis depth: 36.6 in (92.964 cm); 40.5 in. (102.87 cm), including full cosmetics Weight: ● 330.8 lb (148.86 kg) chassis with fans, PDUs, and blanks (as shipped) ● 650 lb (292.5 kg) chassis as shipped, including power shelves and all line cards and route processors |
Power | ● Chassis power supply maximum output capacity: 8.4 kW for DC power supply and 9 kW for AC power supply | ● Chassis power supply maximum output capacity: 8.4 kW for DC power supply and 9 kW for AC power supply |
Environmental conditions | Storage temperature: -40 to 158°F (-40 to 70°C) Operating temperature: ● Normal: 41 to 104°F (5 to 40°C) ● Short-term: 23 to 122°F (-5 to 50°C) Relative humidity: ● Normal: 5 to 85% ● Short-term: 5 to 90% but not to exceed 0.024 kg water per kg of dry air ● Note: Short-term refers to a period of not more than 96 consecutive hours and a total of not more than 15 days in 1 year (a total of 360 hours in any given year, but no more than 15 occurrences during that 1-year period) | Storage temperature: -40 to 158°F (-40 to 70°C) Operating temperature: ● Normal: 41 to 104°F (5 to 40°C) ● Short-term: 23 to 122°F (-5 to 50°C) Relative humidity: ● Normal: 5 to 85% ● Short-term: 5 to 90% but not to exceed 0.024 kg water per kg of dry air ● Note: Short-term refers to a period of not more than 96 consecutive hours and a total of not more than 15 days in 1 year (a total of 360 hours in any given year, but no more than 15 occurrences during that 1-year period) |
Approvals and Compliance
Table 2 lists compliance and agency approvals for both models of the Cisco CRS 8-Slot Single-Shelf System.
Table 2. Approvals and Compliance for Cisco CRS-8/S and Cisco CRS-8/S-B
Feature | Description |
Safety standards | ● UL/CSA/IEC/EN 60950-1 ● AS/NZS 60950.1 ● IEC/EN 60825 Laser Safety ● FDA – Code of Federal Regulations Laser Safety |
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) | ● FCC Class A ● ICES 003 Class A ● AS/NZS CISPR 22 Class A ● CISPR 22 (EN55022) Class A ● VCCI Class A ● IEC/EN 61000-3-2: Power Line Harmonics ● IEC/EN 61000-3-3: Voltage Fluctuations and Flicker |
Immunity (basic standards) | ● IEC/EN-61000-4-2: Electrostatic Discharge Immunity (8-kV contact, 15-kV air) ● IEC/EN-61000-4-3: Radiated Immunity (10V/m) ● IEC/EN-61000-4-4: Electrical Fast Transient Immunity (2-kV power, 1-kV signal) ● IEC/EN-61000-4-5: Surge AC Port (4-kV CM, 2-kV DM) ● IEC/EN-61000-4-5: Signal Ports (1 kV) ● IEC/EN-61000-4-5: Surge DC Port (1 kV) ● IEC/EN-61000-4-6: Immunity to Conducted Disturbances (10 Vrms) ● IEC/EN-61000-4-8: Power Frequency Magnetic Field Immunity (30A/m) ● IEC/EN-61000-4-11: Voltage Dips, Short Interruptions, and Voltage Variations |
ETSI and EN | ● EN300 386: Telecommunications Network Equipment (EMC) ● EN55022: Information Technology Equipment (Emissions) ● EN55024: Information Technology Equipment (Immunity) ● EN50082-1/EN-61000-6-1: Generic Immunity Standard |
Network Equipment Building Systems (NEBS) | This product is designed to meet the following requirements (qualification in progress): ● SR-3580: NEBS Criteria Levels (Level 3) ● GR-1089- CORE: NEBS EMC and SafetyGR-63-CORE: NEBS Physical Protection |
System Capacity
Table 3 shows the system capacity of the Cisco CRS 8-Slot Single-Shelf System.
Table 3. System Capacity for Cisco CRS 8-Slot Single-Shelf System
Number of Interface Slots | Maximum Capacity per Slot | Total Capacity |
8 | 400 Gbps per slot ingress and 400 Gbps per slot egress | 6.4 Tbps per single-shelf system |